The documentation you are viewing is for Dapr v0.11 which is an older version of Dapr. For up-to-date documentation, see the latest version.
Overview of Dapr on Kubernetes
Dapr can be configured to run on any Kubernetes cluster. In Kubernetes the dapr-sidecar-injector and dapr-operator services provide first class integration to launch Dapr as a sidecar container in the same pod as the service container and provide notifications of Dapr component updates provisioned into the cluster. Additionally, the dapr-sidecar-injector also injects the environment variables DAPR_HTTP_PORT and DAPR_GRPC_PORT into all the containers in the pod to enable user defined applications to easily communicate with Dapr without hardcoding Dapr port values.
The dapr-sentry service is a certificate authority that enables mutual TLS between Dapr sidecar instances for secure data encryption. For more information on the Sentry service read the security overview
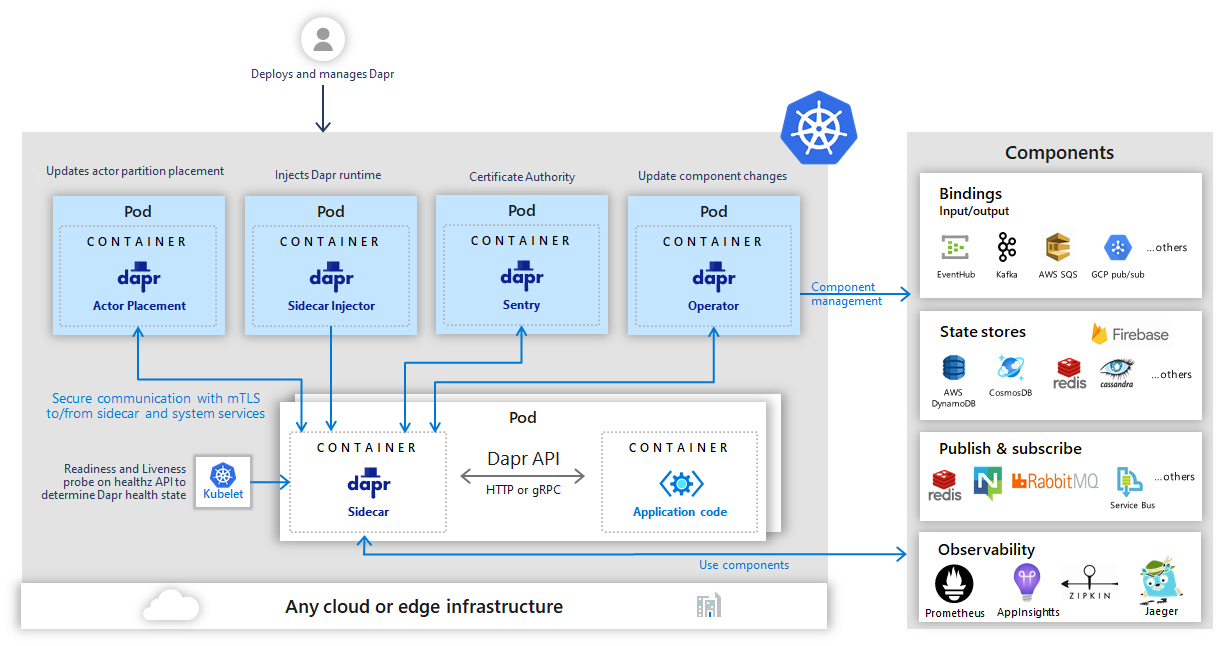
Deploying and running a Dapr enabled application into your Kubernetes cluster is a simple as adding a few annotations to the deployment schemes. To give your service an id and port known to Dapr, turn on tracing through configuration and launch the Dapr sidecar container, you annotate your Kubernetes deployment like this.
annotations:
dapr.io/enabled: "true"
dapr.io/app-id: "nodeapp"
dapr.io/app-port: "3000"
dapr.io/config: "tracing"
You can see some examples here in the Kubernetes getting started sample.
Read Kubernetes how to topics for more information about setting up Kubernetes and Dapr.